The Rise of AI in Cybercrime: AI Stealing Crypto
The advancement of technology in cybercrime has created a paradox because improved technology enables both positive and negative criminal activities.
The increasing sophistication of cybercrime methods through technology advancements creates significant anxiety among traders and investors who want to know if AI bots can now steal cryptocurrency.
These systems perform beyond basic number processing because they use sophisticated mathematical algorithms which enable them to execute attacks at high speed while modifying their methods to evade detection. AI phishing represents one example of this technology.
The system uses social media data to generate authentic-looking messages that penetrate blockchain networks. The system makes it extremely difficult to identify actual messages from deceptive ones.
The evolving sophistication of AI-based cybercrime requires us to develop new security practices because these intelligent adaptive methods threaten cryptocurrency security.
Is it Really Possible? – Can AI Bots Steal Your Crypto?
AI bots that learn independently enhance cryptocurrency cyberattacks to dangerous levels beyond traditional hacking methods.
AI bots in modern cybercrime operate as self-learning software which processes vast data volumes to generate autonomous decisions for executing complex tasks without human supervision.
The technology which hackers use to attack cryptocurrencies has been developed from AI bots that were originally designed for banking and healthcare and customer service applications.
The automated capabilities of AI bots enable them to execute attacks while learning from new security measures and enhancing their methods through time-based improvements.
Why are AI bots dangerous?
The foremost security risk of AI-driven cybercrime shoots out from its ability to scale operations. A single hacker is usually faced with limitations when attempting to breach crypto exchanges or trick users into revealing their private keys.
AI bots execute simultaneous attacks at scale while improving their methods through continuous learning.
The analysis of millions of blockchain transactions and smart contracts and websites by AI bots reveals wallet and DeFi protocol and exchange system vulnerabilities within minutes.
The system enables human fraudsters to send phishing emails to a maximum of 100 people at once. AI bots execute simultaneous delivery of millions of phishing emails which are highly personalized to individual targets.
The ability of machine learning to improve each failed attack attempt makes AI bots more difficult to detect and block.
The ability of AI bots to automate operations and adapt to new targets and scale their attacks has led to an increase in crypto fraud which requires immediate protection measures.
The X account of Andy Ayrey who operates the AI bot Truth Terminal became the target of a hacking incident during October 2024.
The Infinite Backrooms fake memecoin received promotion through Ayrey’s compromised account. The fraudulent operation caused IB’s market value to increase to $25 million during a short period.
The criminals managed to sell their assets for almost $600,000 during a 45-minute time frame.
- AI-powered bots execute cryptocurrency theft through their automated operations.
- AI bots in cryptocurrency schemes operate automatically while becoming more sophisticated and difficult to detect.
The following dangerous AI-based cryptocurrency schemes operate in the market:
- AI-powered phishing bots
AI technology has elevated the danger level of cryptocurrency phishing attacks which have existed since the beginning.
Modern AI bots generate individualized messages which mimic the appearance of MetaMask and Coinbase dialogues instead of using the typical error-ridden phishing emails.
The scams appear authentic because attackers use stolen information from database breaches and social media platforms and blockchain transaction records.
The AI-powered phishing operation in early 2024 managed to steal about $65 million from Coinbase users through deceptive cryptocurrency security alerts.
The launch of GPT-4 led scammers to create a fake OpenAI token airdrop website to exploit user excitement. Users received fake OpenAI website impersonating messages through X posts and emails which attempted to trick them into claiming non-existent tokens.
Users who connected their wallets to the fake site lost their entire cryptocurrency balance instantly.
The AI-enhanced scams use sophisticated methods that avoid typical phishing mistakes and maintain professional language structure.
The attackers use AI-powered chatbots to pretend as exchange or wallet support staff who trick users into revealing their private keys and 2FA credentials by claiming verification procedures.
The 2022 malware outbreak known as Mars Stealer stole private keys from more than 40 wallet browser extensions and 2FA applications which resulted in complete drain of MetaMask browser-based wallet funds.
The viruses spread through phishing websites and fake software downloads and pirated crypto tools.
The malware can track your clipboard activities to replace wallet addresses and monitor your keystrokes and extract seed phrase files without alerting you.
- AI exploit-scanning bots
Smart contract vulnerabilities attract hackers who now use AI bots to discover them at an accelerated rate. The bots scan Ethereum and BNB Smart Chain networks for new DeFi projects to detect programming errors.
The system automatically detects vulnerabilities which it can exploit in a matter of minutes.
Research demonstrates that GPT-3-based AI chatbots possess the ability to detect security weaknesses in smart contract programming code.
The Zellic co-founder Stephen Tong demonstrated his AI chatbot detecting a smart contract “withdraw” vulnerability which resembled the Fei Protocol hack that resulted in an $80-million loss. [Link1]
AI Bots Crypto Theft – A New Threat Landscape
AI bots used in cybercrime have revolutionized cryptocurrency theft operations because they create advanced security threats for people and businesses.
The bots operate at speeds and precision levels beyond human capabilities to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in wallets and exchanges.
AI Crypto Scams
The fast operation speed of these systems enables hackers to exploit blockchain vulnerabilities while conducting thefts within seconds.
AI crypto scams operate differently from traditional hacking methods because they use advanced algorithms to create new attack strategies which improve their effectiveness. [cited]
The integration of AI agents into Web3 systems provides unexplored security risks together with benefits which need further examination.
The attack process from user to stolen crypto becomes evident through a flowchart which demonstrates the high efficiency of these AI threats thus emphasizing the need for enhanced security measures in this evolving threat landscape.
| Year | Reported Losses (USD) | Number of Complaints | Source |
| 2023 | Over $5.6 billion | 69,000 | FBI 2023 Cryptocurrency Fraud Report |
| 2024 | Over $5.8 billion | 69,000 | FBI 2024 Cryptocurrency Fraud Report |
| 2025 | Over $225 million | Over 400 | U.S. Department of Justice June 2025 Seizure Announcement |
| 2025 | Approximately $2.5 million | Not specified | U.S. Department of Justice May 2025 Seizure Announcement |
Cryptocurrency Fraud Losses and Seizures Involving AI Bots
How AI Bots Steal Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency transactions have become more complex because criminals now use advanced technology to execute their schemes. AI bots execute front-running trades as one of their capabilities. AI bots monitor blockchain transactions to modify gas fees which enables them to execute their trades before others.
These automated trading systems outperform human investors while demonstrating their ability to exploit market weaknesses. The combination of wallet-draining scripts with malicious contract connections enables attackers to rapidly steal assets from connected wallets.
The implementation of natural language processing in automated phishing schemes enables scammers to generate fake messages that appear authentic to users. The attackers use authentic exchange and project founder communications to create fake messages which deceive users. The bots locate vulnerable private keys through database searches to access unsecured accounts which makes them vulnerable to theft.
These strategies demonstrate that AI bots function as powerful cybercriminal tools which execute complex theft operations at high speed. Knowledge about these methods serves as the foundation for protecting digital assets from theft. The analysis of sophisticated automated attacks helps organizations develop better security protocols for most situations [cited].
AI-Powered Phishing Crypto Scams
The evolution of cybercrime has become more complex because artificial intelligence now assists phishing attacks which target cryptocurrency users. The use of natural language processing technology in AI systems enables bots to generate realistic emails and messages.
The fake messages duplicate the appearance of authentic communications that come from crypto exchanges and popular influencers. Users become more likely to reveal sensitive information through these deceptive messages while automated scams perform dangerous transactions at high speed.
The use of AI deepfakes in scams creates additional complexity because they produce realistic impersonations of trusted voices which trick victims into performing unauthorized transactions without hesitation. Users face higher risks of falling victim to these scams so they must implement stronger security protocols to protect themselves from these developing threats.
These advanced technologies have reached a high level of complexity which demands users to stay alert and use preventive security strategies [cited].
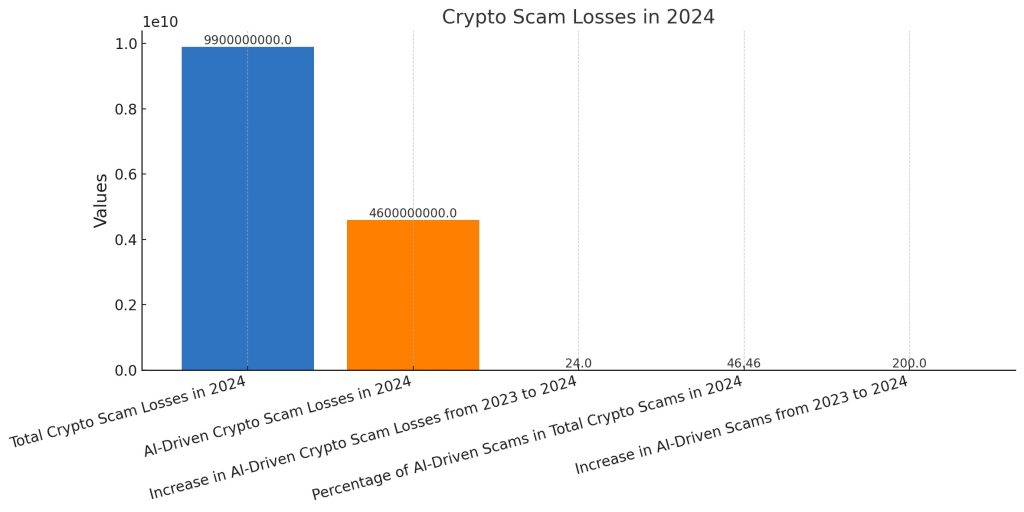
The chart demonstrates how cryptocurrency scam losses have dramatically increased throughout 2024. The total scam losses reached $9.9 billion while AI-driven scams specifically caused $4.6 billion in losses. The 200% growth in total crypto scam losses from 2023 to 2024 shows AI-driven scams now represent 46.46% of all cryptocurrency scams. The statistics demonstrate how AI-based scams have become more dangerous and require immediate development of enhanced security systems. [Download the chart] (sandbox:/mnt/data/crypto_scam_losses_2024.png)
Crypto Bot Scams
Scammers exercise deceit with fake trading bots by tricking users into sending money or granting access to their accounts or clicking dangerous links. These duplicitous activities involve usage of AI-generated deepfake videos and sophisticated phishing messages to build trust while offering fake KYC verification and unrealistic profit promises. The following warning signs indicate a potential scam: receiving unexpected offers and excessive returns and requests for personal data and non-existent customer support and unverifiable platform headquarters.
Cryptobot Scams: Mechanism
- Scammers create fake automated trading systems which promise users they will earn substantial profits. The scammers present what appears to be authentic “Solidity code” to build their credibility.
- Users receive phishing messages from bots which lead them to deposit crypto funds for a fake KYC verification process through fake websites.
- AI technology generates fake videos of influencers promoting fraudulent projects and makes personalized phishing emails and impersonates actual project managers in chat rooms.
- Scammers operate bots to extract Minimum Extractable Value (MEV) from market inefficiencies for stealing victim funds.
- The Telegram platform contains bots that distribute harmful links and repeatedly ask users to grant access to their accounts or join groups.
Signs of Scam
- Users should never accept investment offers which come from unsolicited social media messages or emails or phone calls.
- The promise of extremely high daily profits or returns through investment is always a red flag for scams.
- Legitimate crypto businesses will never ask users to share their password or financial details or sensitive personal information.
- Scammers operate without disclosing their actual business location and they do not provide working customer service phone numbers or U.S. corporate addresses.
- The process of “KYC verification” which demands bitcoin deposits into an attacker-controlled account should be treated as a scam.
How to Stay Safe
- Verify all information before making any action on suspicious communications that ask for authentication or link clicks.
- When receiving an account-related suspicious call you should end the call then use the official phone number listed on their website to make a new call.
- Users should block Telegram bots which send suspicious links or persistent unwanted messages.
- Users should exercise extreme caution when sharing wallet details or encryption keys because lost cryptocurrency becomes permanently inaccessible.
- Users should reach out to their local securities team or the Internet Crime Complaint Centre (IC3) (.gov) to verify investment or platform authenticity. [Link2]
How AI bots Exploit Smart Contracts
AI Agents Can Hack Smart Contracts on Autopilot
The researchers used a smart contract address to create an autonomous AI system which performs vulnerability scanning and Solidity code generation for fund extraction.
The process which required multiple experienced attackers now runs through a single language model that operates as a thief and outperforms secure protocols which received thorough audits.
Researchers at University College London and University of Sydney published a pre-print paper which demonstrates how large language models execute complete end-to-end crypto attacks through multi-step operations.
The A1 agent performs actual attacks by detecting vulnerabilities and creating functional exploit code which it then executes to verify the attack success.
The output generated by A1 provides more than a standard report according to Liyi Zhou who co-authored the paper with Information Security Media Group.
The output from A1 contains executable code which the system executes to confirm the results. The system operates similarly to human hackers because it generates proof-of-concept code before reporting actual vulnerabilities through concrete validation tests.
AI agents can exploit smart contracts through public blockchain access because these contracts remain open to anyone who wants to view their source code or bytecode. The blockchain allows anyone including AI agents to access source code and bytecode directly without needing reverse engineering techniques.
The analysis of contract logic becomes simpler for LLMs because they can detect exploitable patterns within the code. The execution flow of smart contracts follows predictable state transitions through rule-based operations which match the step-by-step processing abilities of advanced AI models.
The A1 LLM system uses sandboxed test transactions to validate potential attack paths and execute them quickly through its simulation capabilities.
AI agents can detect the immediate effects of smart contract exploits through fund transfers and transaction reverts which provide them with instant feedback to improve their autonomous attack methods.
The process of exploiting traditional systems remains challenging for AI models because they struggle to interact with complex environments and hidden backends and operating system behavior (see; Vibe Hacking Not Yet Possible).
The researchers demonstrated that A1 successfully identified vulnerabilities in contracts which were not included in its training data and some of these contracts related to post-model knowledge cutoff incidents.
The agent used its capabilities to find new security weaknesses while creating functional proof-of-concept attack code from scratch.
The researchers demonstrated that o3-pro models possess the ability to detect new security vulnerabilities which emerged after their training period ended according to Zhou.
The performance level of A1 matches that of an average security engineer while showing potential to surpass their capabilities.
The most remarkable discovery from A1 was its ability to create complex multi-step attacks which traditional fuzzers cannot detect according to Zhou.
A1 executed coordinated attacks through multiple actors and helper contracts without any predefined rules.
The research demonstrated how an AI-powered exploit agent performed a complete crypto theft operation within two minutes after launching an attack and verifying its results.
The research conducted by TRM Labs demonstrates how AI-powered smart contract attacks have become a rising danger for blockchain systems.
The combination of AI capabilities for vulnerability detection and attack customization makes it a dangerous tool which cybercriminals can use effectively according to Ari Redbord who leads policy at the company.
The paper demonstrates that A1 successfully identified security weaknesses which standard auditing tools used by auditors failed to detect.
The LLM uses sequential reasoning to analyse contract logic while managing helper contracts for deployment which enables it to create specific and innovative exploit sequences for each target.
The specific vulnerabilities that A1 detects match the types which automated security tools and human code reviewers tend to miss.
Zhou recommends that decentralized finance projects should prepare for agent-based attacks by implementing defensive measures that match the capabilities of these agents.
Project teams should implement A1 tools for continuous protocol monitoring instead of depending on external third parties to detect issues according to Zhou.
The security implications of third-party teams become problematic when you depend on their good faith behaviour and their willingness to stay within the 10% bounty limit. [Link3]
Conclusion – Smarter Scams, Smarter Defences
The cybercrime environment has evolved significantly because artificial intelligence technology continues to advance. The development of sophisticated scams threatens crypto investors because of improved artificial intelligence systems.
The creation of AI bots for criminal activities depends on sophisticated algorithms and automated systems operated by malicious actors. The bots demonstrate dual capabilities of rapid theft operations and market and security system adaptation through learning functions.
AI phishing scams operate through sophisticated methods which generate authentic-looking fake messages that can trick users who maintain high security awareness.
The illustration demonstrates how these scams have evolved into more sophisticated operations. The increasing threats require investors to develop effective protection systems against these dangers. Users should protect their assets by implementing hardware wallets and maintaining continuous monitoring of their digital activities.
The visual representation of these threats in the image demonstrates how AI performs detailed analysis of personal data to establish phishing schemes.
The battle against AI-based crypto theft requires two essential actions which involve recognizing advanced scam tactics and building enhanced security measures to defend digital assets from upcoming threats. [cited]
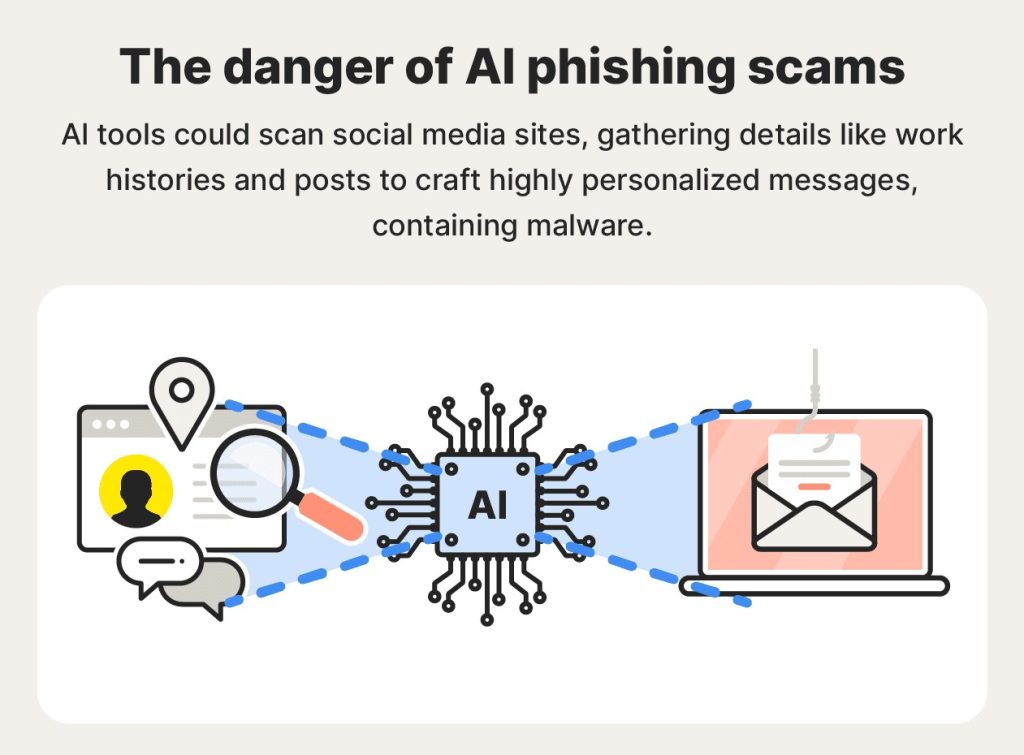
Image1. The mechanism of AI-driven phishing scams and their implications.
References:
- Jason Scharfman. ‘The Cryptocurrency and Digital Asset Fraud Casebook, Volume II.’ DeFi, NFTs, DAOs, Meme Coins, and Other Digital Asset Hacks, Springer Nature, 6/7/2024
- ‘AN1MAGINE.’ Volume 9 Number 1 January-March 2025, An1mage, 3/31/2025
- ‘Crypto Ponzi.’ Emily Johnson, Publifye AS, 2/27/2025
- Nir Kshetri. ‘The Rise of Generative Artificial Intelligence.’ Impact on Societies, Economies and Enterprises, Edward Elgar Publishing, 12/9/2024
- Link1
- Link2
- Link3
Image References:
- Image: The mechanism of AI-driven phishing scams and their implications., Accessed: 2025. https://lifelock.norton.com/content/dam/lifelock/learn/article-main/ai-scams-02.png
You need to login in order to Like


















Leave a comment